Integrating Redux with Lit Elements for Web Components
Web components with Lit Element provide a powerful way to create reusable UI elements. Adding Redux for state management makes them even more powerful. This guide demonstrates how to integrate Redux with Lit Elements for efficient state management in your web components.
## Project Setup
First, let’s set up our project using the custom generator we created earlier that provides a complete development environment.
# Install the generator globally
npm install -g generator-lit-sass-rollup-openwc-starter
# Generate your project
yo lit-sass-rollup-openwc-starter
# Follow the instructions on-screen to create your own component.
# My component's name is redux-with-lit.
# Navigate to your project
cd redux-with-lit
# Install Redux dependencies
npm install redux @reduxjs/toolkit
## Project Structure
Create the following folder structure for Redux integration:
src/
├── models/ # Model definitions
├── store/ # Redux store and slices
## Setting Up the Redux Store
Let’s create our Redux infrastructure step by step:
### 1. Define the State Model
Create models/example-state-model.ts:
export interface ExampleStateModel {
name: string;
color: string;
}
### 2. Create the Redux Slice
The Redux slice defines how our state changes in response to actions. Let’s break down what’s happening in store/example-store.ts:
import { PayloadAction, createSlice } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
import { ExampleStateModel } from "../models/example-state-model";
// Function to update specific fields in state
const updateExampleState = (state: any, action: PayloadAction<any>) => {
// Create deep copy to maintain immutability
let newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state));
if (action.payload != undefined) {
// Check if we're updating a form field with value property
if (newState[action.payload.fieldName]?.value != undefined) {
// Update form field value
newState[action.payload.fieldName].value = action.payload.fieldValue;
} else {
// Update regular field directly
newState[action.payload.fieldName] = action.payload.fieldValue;
}
}
return newState;
};
// Function to replace entire state
const upsertExampleState = (state: any, action: PayloadAction<ExampleStateModel>) => {
// Create deep copy to maintain immutability
let newState = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(state));
if (action.payload != undefined) {
// Replace entire state with new payload
newState = action.payload;
}
return newState;
};
// Create Redux slice with reducers
const { actions: exampleActions, reducer: ExampleState } = createSlice({
name: "ExampleState", // Unique name for this slice
initialState: {}, // Empty initial state
reducers: {
updateExampleState, // For partial updates
upsertExampleState, // For complete state replacement
},
});
export { exampleActions, ExampleState };
What’s Happening Here?
-
State Update Functions:
updateExampleState: Handles granular updates to specific fieldsupsertExampleState: Performs complete state replacement
-
Immutability Handling:
- Uses
JSON.parse(JSON.stringify())for deep cloning - Ensures state updates are immutable
- Uses
-
Action Types:
- Update:
{ fieldName: string, fieldValue: any } - Upsert: Complete
ExampleStateModelobject
- Update:
### 3. Configure the Store
The store configuration in store/app-store.ts sets up the Redux infrastructure:
import { combineReducers } from "redux";
import { configureStore } from "@reduxjs/toolkit";
import { ExampleState } from "./example-store";
// Combine reducers for scalability
const rootReducer = combineReducers({
ExampleState
});
// Create store with Redux Toolkit's configureStore
export const store = configureStore({
reducer: rootReducer,
});
// Export initial state
export const state = store.getState();
What’s Happening Here?
-
Store Setup:
combineReducers: Combines multiple slice reducersconfigureStore: Sets up Redux with best practices- Automatically adds Redux DevTools
- Includes common middleware
- Enables development checks
-
State Structure:
{
ExampleState: {
name?: string;
color?: string;
// Other fields as needed
}
}
### 3. Let’s See it in Action
## Editing our Lit Element Component with Redux
Let’s use our hello-world component that demonstrates Redux integration. We’ll edit the two existing files:
### HTML Template
We add three buttons to the existing HTML to show the state managment functionality.
Edit the components/hello-world/html/hello-world.html:
<!-- Existing displayed text -->
<h1 id="heading">${this.stringToDisplay}</h1>
<!-- Button to Upsert the state -->
<button @click=${this.upsertExampleState}>Upsert Example State</button>
<!-- Button to Update the state -->
<button @click=${this.updateExampleState}>Update Example State</button>
<!-- Button to Get the state and Apply the change -->
<button @click=${this.getExampleState}>Change(Get Example State)</button>
### Component Logic
We add a new property and define the binding functions.
Edit the components/hello-world/hello-world.ts:
import { css, LitElement, unsafeCSS } from 'lit';
import { customElement, property } from 'lit/decorators.js';
import template from './html/hello-world.html';
import componentStyles from '../../styles/component-styles.scss';
import { store } from '../../store/app-store';
import { exampleActions } from '../../store/example-store';
import { ExampleStateModel } from '../../models/example-state-model';
@customElement('hello-world')
export class HelloWorld extends LitElement {
@property() stringToDisplay = 'Hello, World!';
/** New Property to Specify the color of the text **/
@property() color = '';
static get styles() {
return css`
${unsafeCSS(componentStyles)}
`;
}
/** Calling Functions **/
/**
* Retrieves the current state from Redux store and updates the component's UI.
* Gets the name and color from ExampleState and applies them to the heading element.
*/
getExampleState() {
const stateResponse = store.getState()?.ExampleState as ExampleStateModel;
this.stringToDisplay = stateResponse.name;
this.shadowRoot!.getElementById('heading')!.style.color = stateResponse.color;
}
/**
* Updates a specific field in the Redux state.
* In this example, updates only the color field to 'blue'.
* Uses the updateExampleState action which handles partial state updates.
*/
updateExampleState() {
const stateObject = {
fieldName: 'color',
fieldValue: 'blue',
};
store.dispatch(exampleActions.updateExampleState(stateObject));
}
/**
* Replaces the entire state with new data.
* Sets both name and color properties using the upsertExampleState action.
* This is useful when you need to update multiple fields simultaneously.
*/
upsertExampleState() {
store.dispatch(exampleActions.upsertExampleState({
name: 'My Dummy Name',
color: 'red'
}));
}
render() {
return template.call(this);
}
}
## 4. Running the Application
Build and serve your application:
npm run build
npm run serve
Visit http://localhost:8000/demo to see your component in action.
## 5. Testing the Redux Integration
The component demonstrates three key Redux operations:
- Upsert State: Click the “Upsert Example State” button to completely replace the state with new data
- Update State: Click “Update Example State” to modify just the color property
- Get State: Click “Change” to retrieve and display the current state
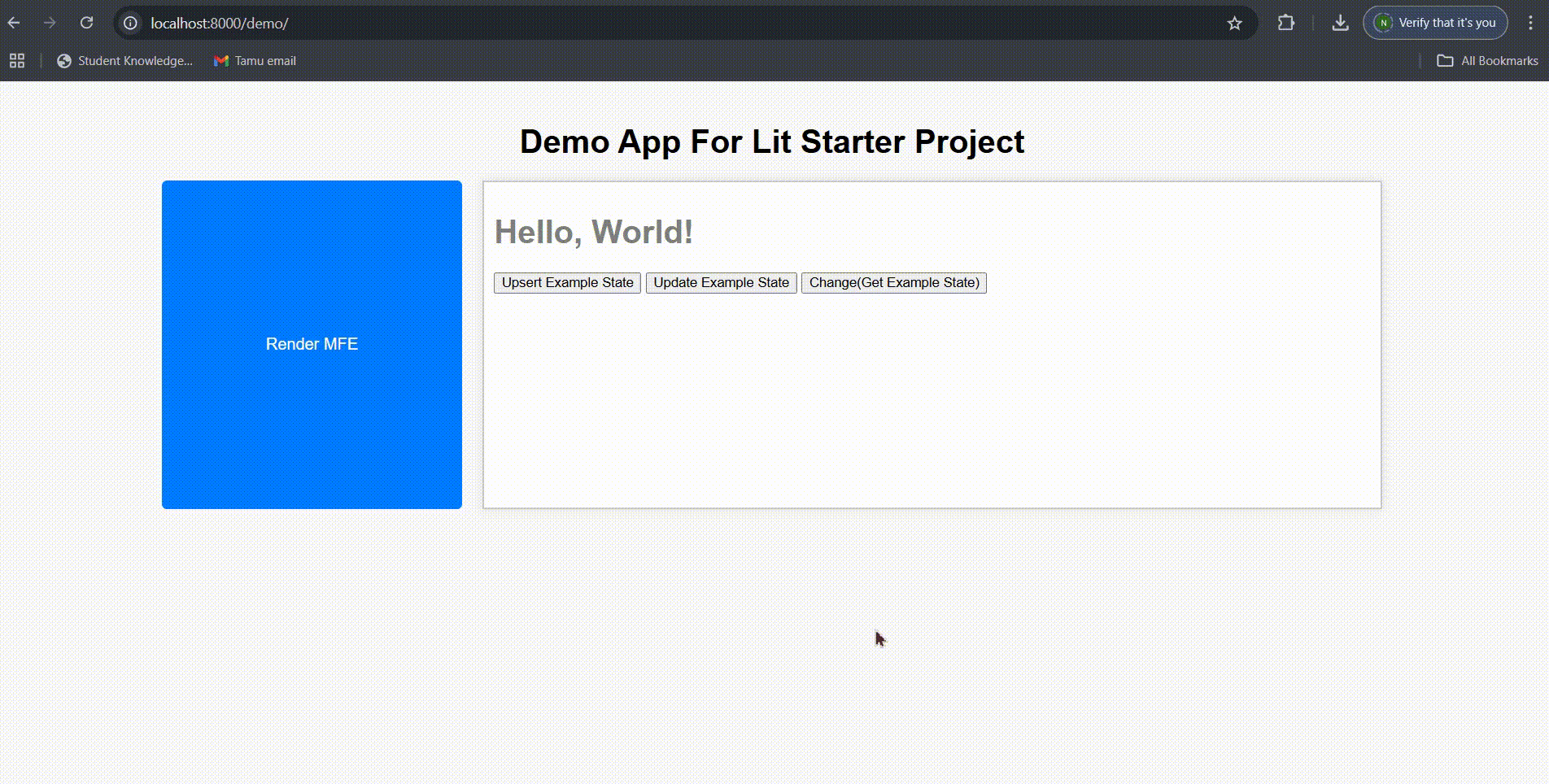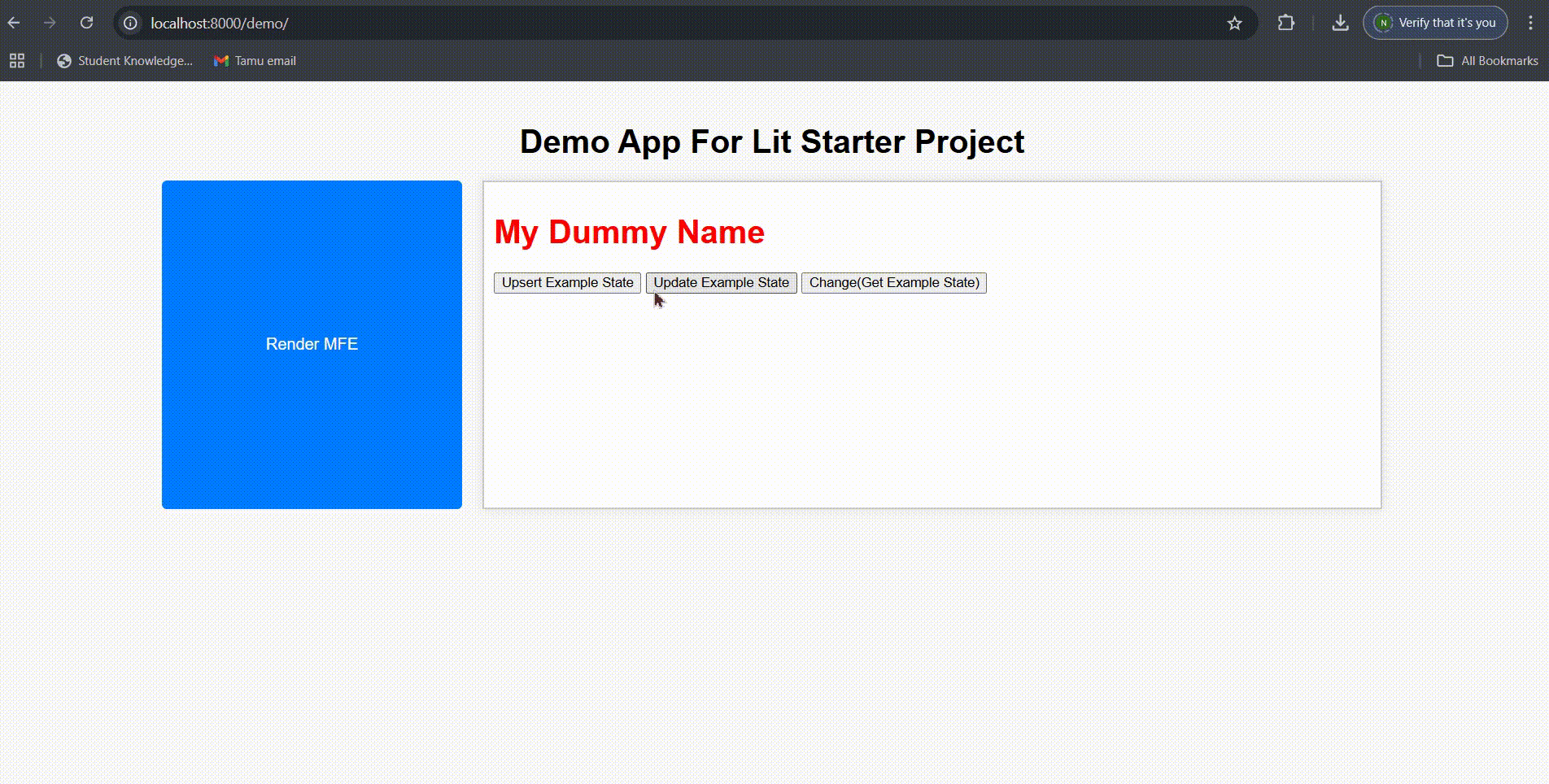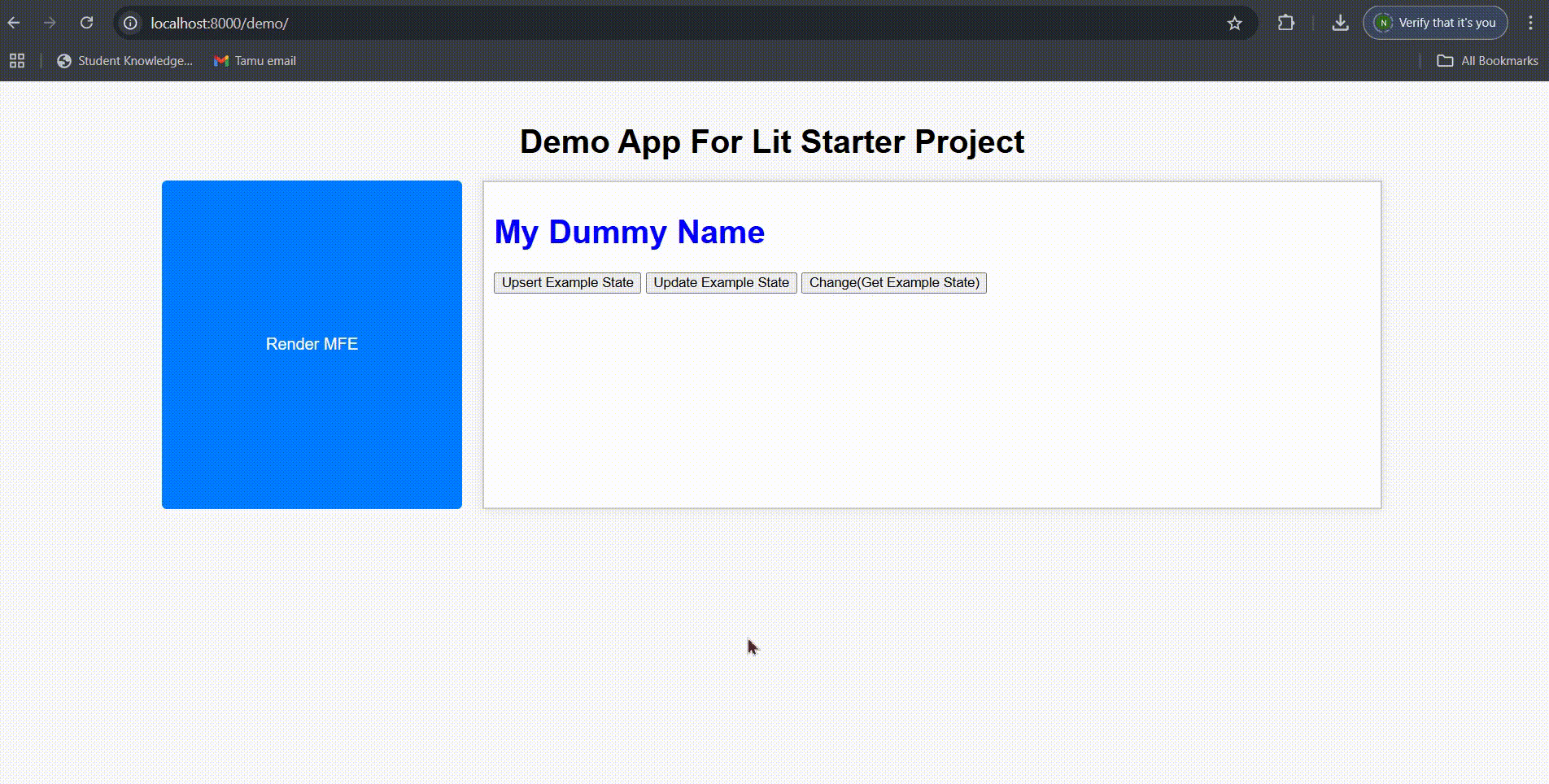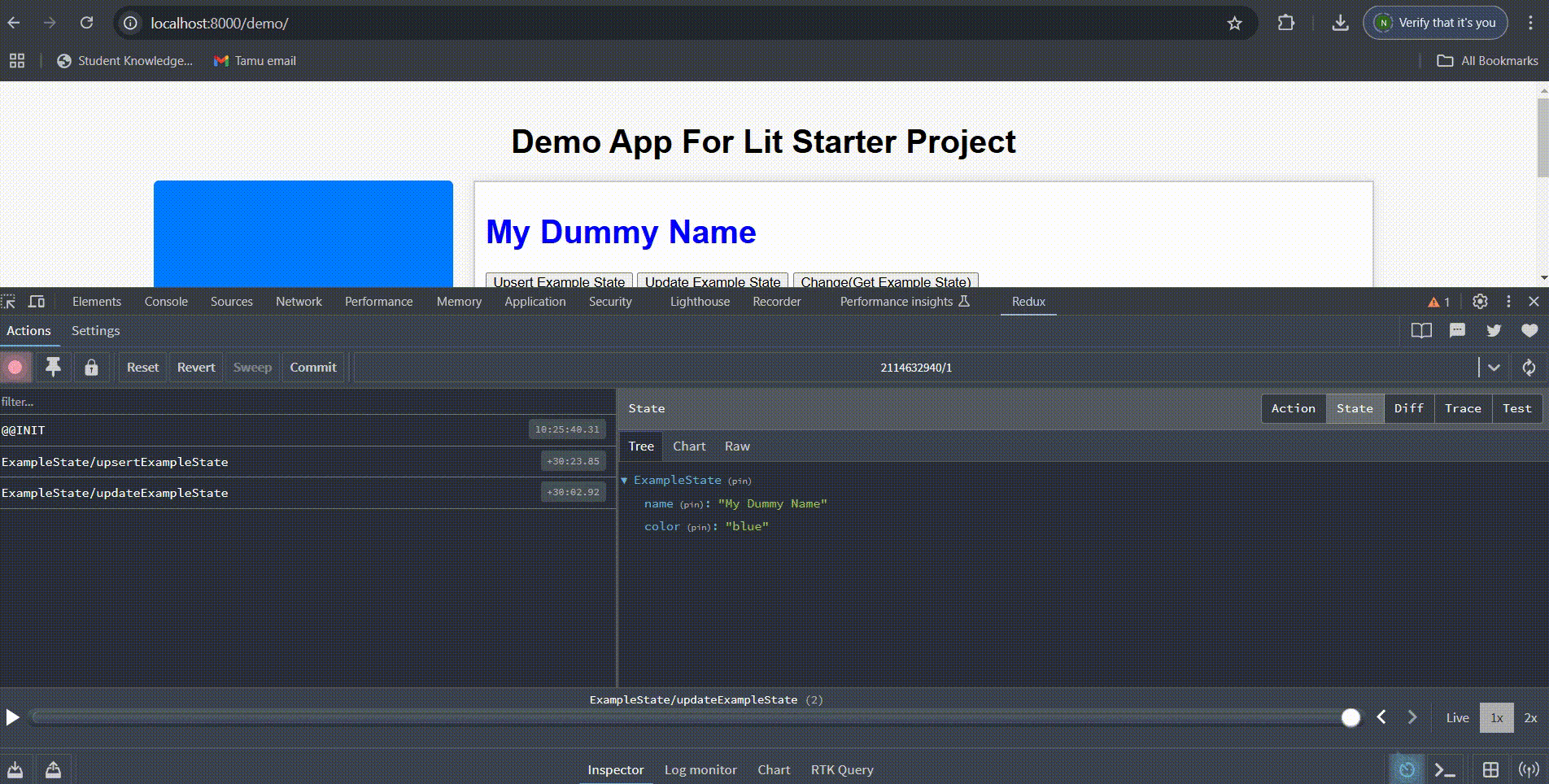
## 6. Debugging with Redux DevTools
For debugging, install the Redux DevTools Chrome Extension. This provides real-time state inspection and action tracking.
## Next Steps
- Explore more complex state models
- Add middleware for side effects
- Implement state selectors
- Add error handling
Visit the GitHub repository for all the code.
This integration demonstrates how Redux can provide robust state management for Lit Element web components while maintaining their modular and reusable nature.